Minerals are essential to daily life, used in objects ranging from tools to large structures.Life processes and industrial activities rely on minerals for functionality and development.
What are Minerals?
- Minerals are naturally occurring, homogeneous substances with a definable internal structure.
- Found in various forms, from the hardest diamond to the softest talc.
- Geologists and geographers study minerals for their formation, distribution, and economic uses.
Modes of Occurrence of Minerals
Minerals are found in ‘ores.’ An ore is an accumulation of any mineral mixed with other elements.
- The ore must have sufficient mineral concentration to make its extraction economically viable.
- Their formation/structure dictates the relative ease and cost of extraction.
Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks
- Found in veins and lodes within cracks and crevices, faults and joints.
- They form when minerals in molten and gaseous forms are forced upward through cavities towards the earth’s surface, and cool and solidify as they rise.
- Examples: Tin, Copper, Zinc, Lead.
Sedimentary Rocks
- Occur in horizontal layers or beds , that’s why they are called ‘sedimentary’.
- Form by deposition, accumulation and concentration in horizontal strata.
- Coal and some iron ores are formed when they remain under grea heat and pressure.
- Salts form as a result of evaporation, specially in arid regions.
- Examples: Potash salt sodium salt, coal, gypsum.
Residual Masses
Forms through the decomposition of surface rocks, where soluble constituents are removed, leaving behind a residual mass of weathered material containing ores.
Examples: Bauxite
Alluvial Deposits
Some minerals may be found as alluvial deposits, generally in the sands of valley floors, and base of hills.
Called ‘placer deposits’, generally contains minerals, which are not corroded by water.
Precious metals are generally found as alluvial deposits.
Examples: Gold, Silver, Platinum, Tin
Ocean Waters
The ocean waters contains vast quantities of minerals, but since they are too diffused in the ocean they aren’t economical to extract.
Examples: Common salt, Magnesium, Bromine
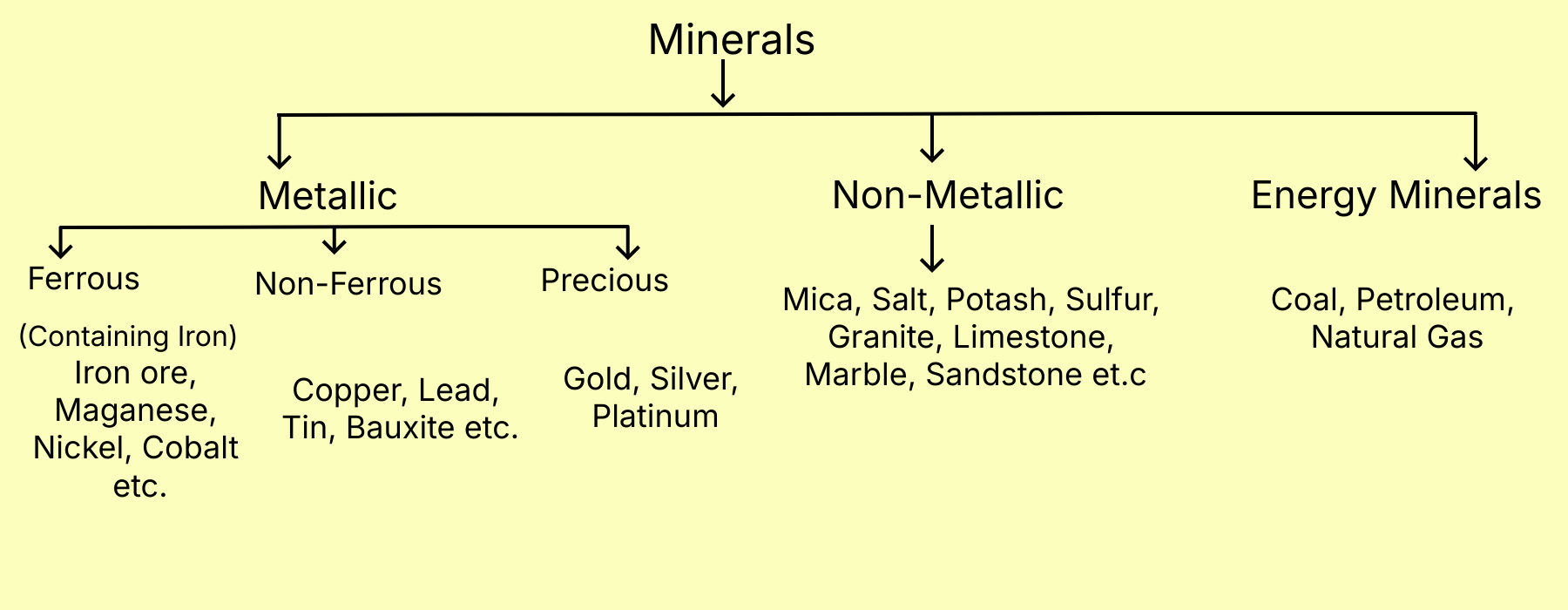
Classification of Minerals
Major Minerals and Their Distribution
Ferrous Minerals
Iron Ore:
Types:
Magnetite Can have upto 70% iron content, has magnetic qualities, and it’s widely used in the electrical industry.
Hematite : This has the highest quantity, but it has a lower iron content of about 50%-60%.
Major States: Odisha, Chhattishgarh, Karnataka and Jharkhand.
Major belts: Odisha-Jharkhand, Durg-Bastar, Ballari-Chitradurga, Maharashtra-Goa.
Manganese:
- Used in steel manufacturing, bleaching powder, insecticides, paints.
- About 10kg of manganese is required to make 1 tonne of steel.
- Major producers: Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra
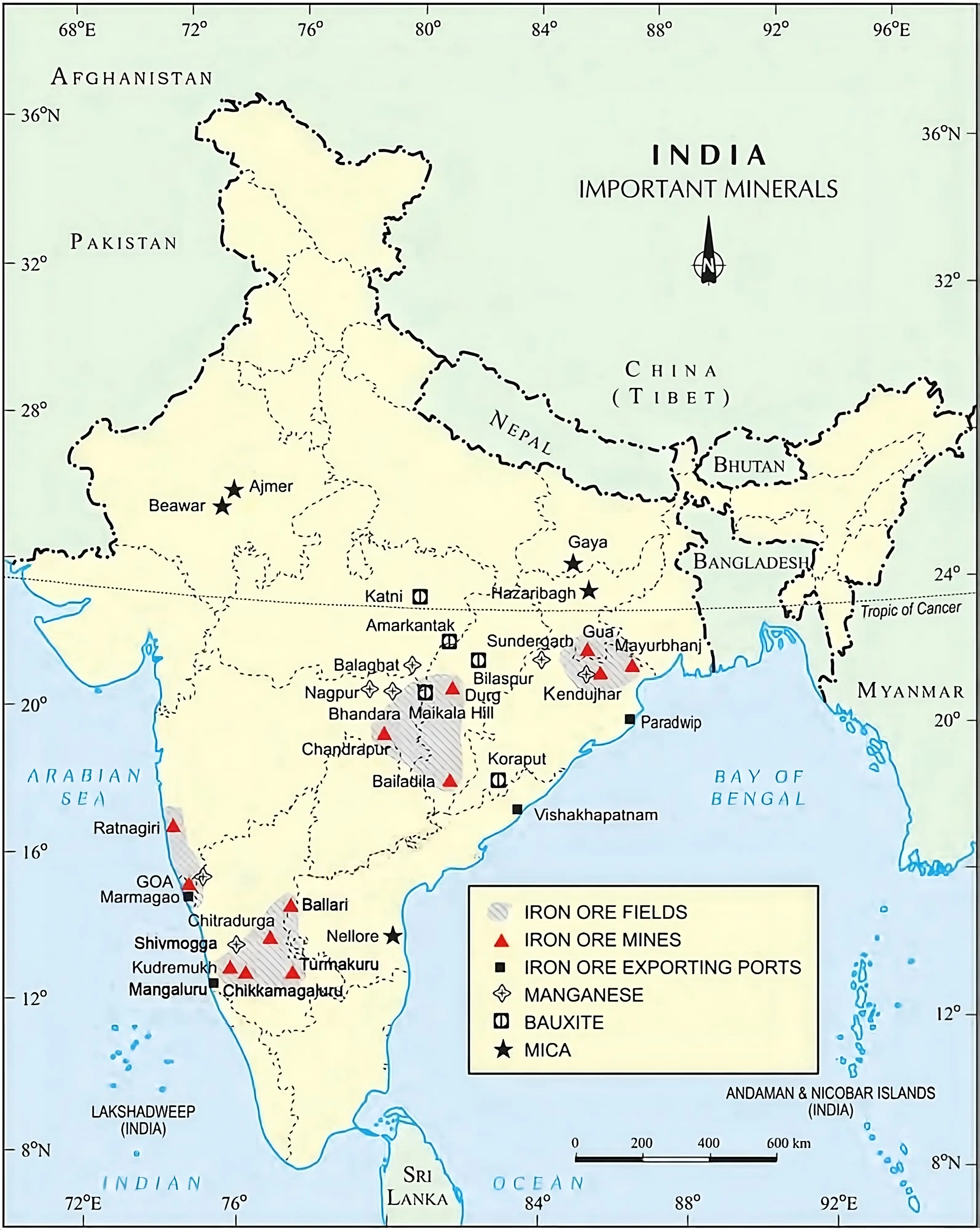
Iron Ore Distribution in India.
Non-Ferrous Minerals
Copper:
- It’s critically deficient in the Indian reserve.
- Major Producers: Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Jharkhand.
Bauxite:
Several ores contain aluminium. But bauxite is the mineral from which aluminium is produced.
Combines the strength of metals such as iron, with extreme lightness.
Good conductor of heat and electricity, highly malleable.
Formed from the decomposition of a wide variety of rocks rich in aluminium silicates.
Mainly found in the Amarkantak plateau region, Bilaspur-Katni plateau region, Maikal hills. As a state, Odisha leads in production.

Production of Manganese, state-wise share, 2018–19.
Non-Metallic Minerals
Mica
Splits into thin sheets.
Sheets are so thin that thousands can form a mica sheet just a few centimeters high.
Low power loss , Insulating , High voltage resistance.
Crucial for the electric and electronic industries.
Mainly found in: Chota Nagpur Plateau (Northern edge), Jharkhand Koderma-Gaya-Hazaribagh belt, Rajasthan Around Ajmer, Andhra Pradesh: Nellore mica belt
Found in Jharkhand, Rajasthan, and Andhra Pradesh.
Rock Minerals
- Limestone
- Found with with rocks composed of calcium carbonates or calcium and magnesium carbonates.
- Most found in sedimentary rocks.
- Essential for making cement and iron smelting.
Hazards of Mining
- Health risks: Pulmonary diseases from dust and fumes.
- Environmental impacts: Water contamination, land degradation, and deforestation.
Conservation of Minerals
Total volume of workable mineral deposits is an insignificant fraction i.e. 1% of the earth’s crust.
Minerals are finite and non-renewable.
Conservation strategies:
- Recycling metals.
- Using scrap metals and other substitutes
- Using low-grade ores efficiently.
Energy Resources
Conventional Sources
Coal:
Coal forms due the compression of plant material over millions of years. Thus, it’s found in many forms depending on the degree of compression and temperature.
- Types:
- Lignite: Low-grade, soft with high moisture content, brown coal. Mainly found in Tamil Nadu. Used for generation of electricity.
- Bituminous: Buried deep with high temperatures. Used for smelting iron.
- Anthracite: Highest quality hard coal.
- Decaying plants in swamps produce peat. Peat may turn into lignite.
- Major fields: Damodar Valley, Godavari Valley.
- Tertiary coals: Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, and Meghalaya.
- Types:
Petroleum:
Petroleum is the second major energy source in India after coal.
Provides fuel for heat and lighting.
Lubricants, textiles, fertilizers, and various chemicals are manufactured from its raw materials.
Mainly found in anticlines and fault traps in tertiary rock formations.
Key areas: Ankeleshwar, Maharashtra. Mumbai High, Gujarat, and the oldest oil producing state, Assam.
Natural Gas:
It is used as fuel in power sector to generate electricity, for heating purpose in industries, as raw material in chemical, petrochemical and fertilizer industries, as transport fuel and as cooking fuel.
Found in association with petroleum deposits (e.g., Krishna-Godavari Basin).
Used as transport fuel (CNG) and cooking fuel (PNG) at homes.
- Electricity:
- Hydroelectricity is a form of renewable energy, which is generated from fast flowing water.
- Thermal power stations use non-renewable energy sources to generate electricity like coal and petroleum.
Non-Conventional Sources
Solar Energy:
- Ideal for rural India.
Wind Power:
Largest farms in Tamil Nadu and Gujarat.
Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Kerala, Maharashtra and Lakshadweep have important wind farms as well.
Bio Gas:
- Eco-friendly energy from organic waste.
Geothermal and Tidal Energy:
- Ocean tides can be used for electricity generation.
- Experimental setups for geothermal energy have been setup in Himachal Pradesh, Ladakh.
Sustainable Energy Use
Energy is crucial for economic development, powering sectors like agriculture, industry, transport, and households. Since Independence, rising energy demand has been linked to the country’s growth.
India is among the least energy-efficient nations, requiring careful use of limited resources.
- Promote renewable energy.
- Conserve energy by using efficient technologies and reducing wastage.